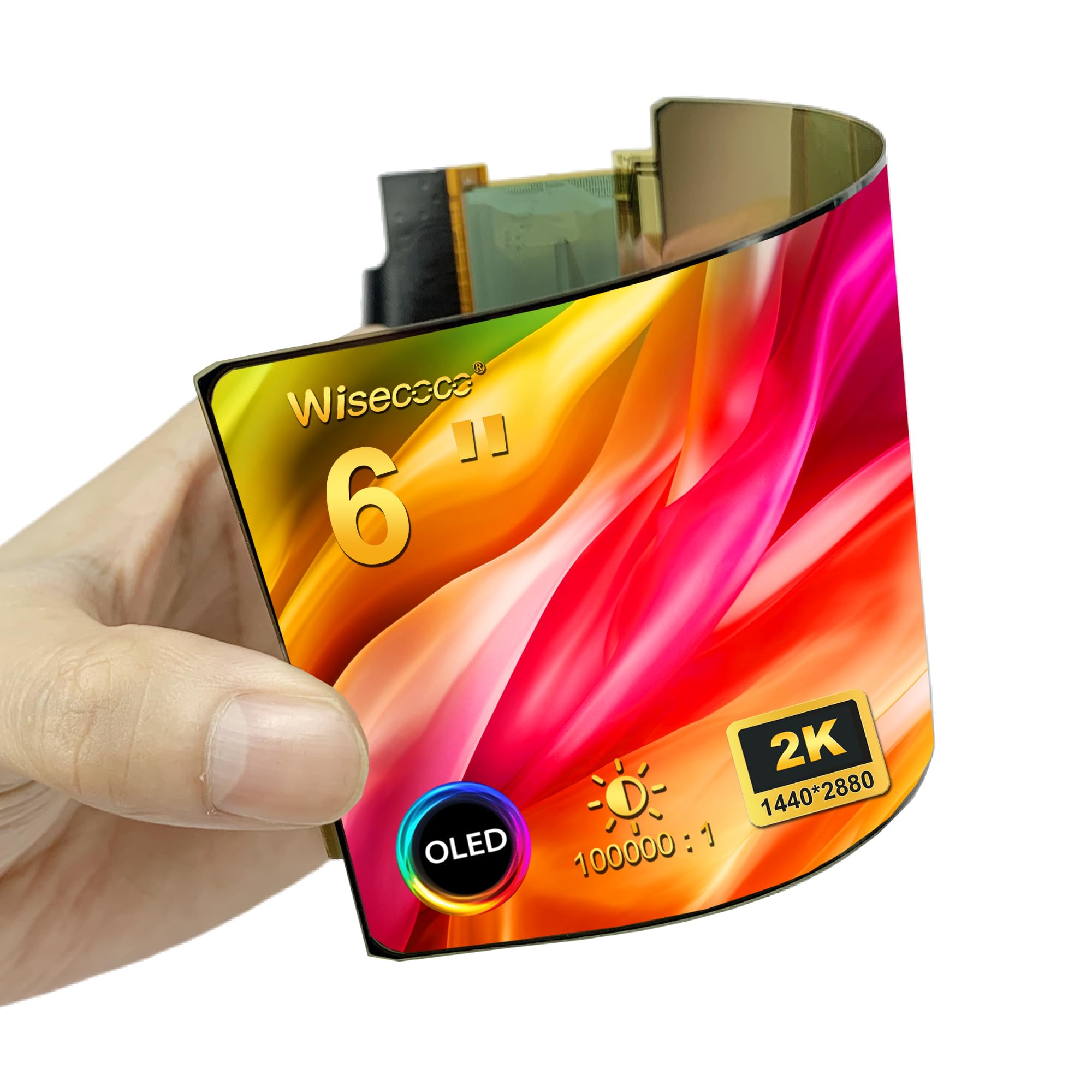
OLED technology, which stands for Organic Light Emitting Diodes, represents a significant advancement in display technology. It has revolutionized the way we experience visual media across various devices, from televisions and smartphones to wearable technology. Here's an in-depth exploration of what OLED technology is, how it works, its advantages, applications, and its potential future.

What is OLED?
OLED is a type of display technology that uses organic compounds to emit light when an electric current is applied. Unlike traditional LCD displays that require a backlight, OLED displays produce their own light. This trait allows for thinner design profiles, greater contrast ratios, and more vibrant colors.
The OLED panel consists of several layers of organic materials sandwiched between two electrodes: a cathode and an anode. When electricity flows through these layers, the organic compounds emit light. The color of the emitted light depends on the thickness and composition of the organic materials used.
How Does OLED Work?
The fundamental principle behind OLED technology is electroluminescence. Here’s a brief breakdown of the OLED structure and how it operates:
- Substrate: The base layer that may be made from glass or flexible plastic, supporting the OLED structure.
- Anode: This layer is transparent and allows light to pass through. It removes electrons from the organic compounds when a voltage is applied.
- Organic Layers: The organic compounds are crucial for light emission. There are typically two layers:
- The hole transport layer (HTL), which carries positive charge holes.
- The electron transport layer (ETL), which carries negative charges (electrons).
- Cathode: The top electrode, which is usually made of a reflective material, injects electrons into the organic layers.
When a voltage is applied, electrons move from the anode to the cathode, recombining with holes in the organic layers, resulting in the emission of light. Different compounds emit different colors, which can be combined to produce full-color images.
Advantages of OLED Technology
OLED displays come with numerous advantages that make them an appealing choice for various applications:
- Superior Picture Quality: OLED technology delivers deeper blacks and brighter whites, thanks to its ability to turn off individual pixels completely. This results in an infinite contrast ratio.
- Vibrant Colors: OLED screens can reproduce a wider color gamut compared to traditional LCDs, providing more vivid and lifelike images.
- Thin and Flexible Design: Because they do not require a bulky backlight, OLED displays can be made thinner and even flexible, allowing for innovative designs in smartphones and televisions.
- Wide Viewing Angles: OLED technology maintains color accuracy and brightness even at wide viewing angles, making it ideal for shared viewing experiences.
- Faster Response Times: OLEDs offer faster refresh rates and response times, reducing motion blur in fast-paced scenes—an essential feature for gaming and action films.
- Energy Efficiency: When displaying dark images or colors, OLED panels consume significantly less power compared to conventional displays, making them more energy-efficient.
Applications of OLED Technology
The versatility of OLED technology has led to its widespread adoption in numerous applications:
- Televisions: OLED televisions have gained popularity for their exceptional picture quality, with brands like LG and Sony leading the market.
- Smartphones: Major manufacturers, including Apple, Samsung, and Google, incorporate OLED displays in their flagship devices to enhance the user experience.
- Wearable Devices: Smartwatches and fitness trackers employ OLED screens for their vibrant displays
and low power consumption, allowing extended battery life.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): The rapid response times and high resolution of OLED make them suitable for immersive VR and AR applications.
- Automotive Displays: As the automotive industry embraces digital interfaces, OLED technology is being integrated into dashboards and infotainment systems for improved visuals.
Challenges Facing OLED Technology
Despite its many advantages, OLED technology is not without challenges:
- Burn-In Issues: Prolonged display of static images can lead to permanent ghosting or burn-in, where remnants of previous images remain visible.
- Cost: The manufacturing process for OLED displays can be more expensive than traditional LCDs, leading to higher prices for consumers.
- Lifespan Concerns: While OLED technology has advanced significantly, blue OLEDs tend to degrade faster than red or green, potentially affecting the longevity of screens.
The Future of OLED Technology
The future of OLED technology appears bright, with ongoing research aimed at addressing its limitations. Innovations in materials and production techniques hold the potential to improve lifespan, reduce costs, and enhance performance.
- MicroLED Technology: Emerging as a competitor, MicroLED uses tiny self-emitting LEDs to create displays with similar advantages to OLED, albeit with improved brightness and longevity.
- Flexible Displays: The development of flexible OLEDs could lead to new form factors in electronics, including rollable TVs and foldable smartphones.
- Sustainable Practices: As environmental concerns rise, manufacturers are investigating more sustainable production methods for OLED technology to meet consumer and regulatory demands.
In conclusion, OLED technology has emerged as a transformative force in the world of displays, offering exceptional picture quality, design flexibility, and energy efficiency. As it continues to evolve, OLED stands poised to define the future of visual experiences across various industries. Whether through advancements in existing applications or the emergence of completely new uses, OLED technology is set to remain at the forefront of display innovations for years to come.