Helping the needy in Venezuela with ،Tether
TRC20 - USDT
TDYwNu4SbmPaLuJEw3oLQNFFyAmqA3Yvog
The Needy Population in China
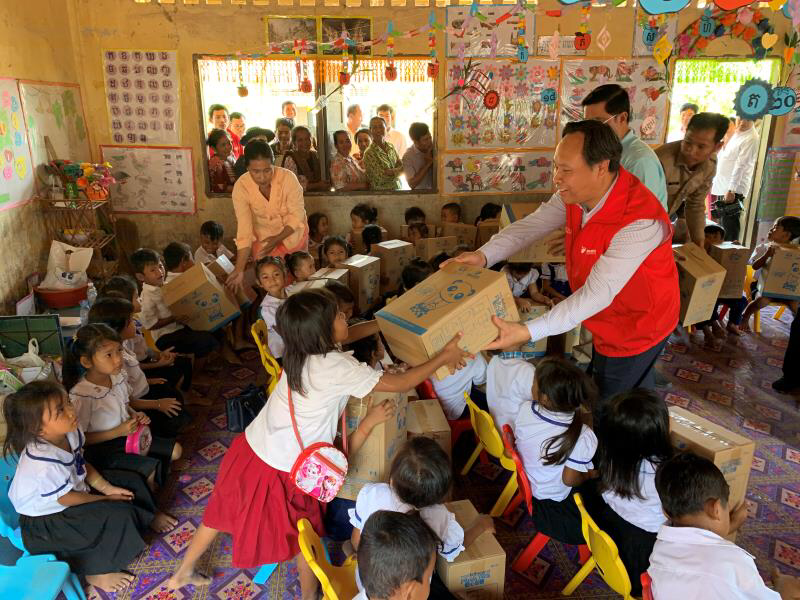

China, as one of the world’s largest economies, has undergone remarkable economic growth over the past few decades. Despite this development, poverty and neediness remain significant challenges, especially in certain rural and remote areas. This article examines the situation of the needy in China, their causes, struggles, and the efforts taken by the government to alleviate poverty.
Overview of the Needy Population in China
While China has lifted hundreds of millions out of extreme poverty since the 1980s, many people still live in conditions that can be described as needy or vulnerable. Poverty in China is mainly concentrated among rural residents, ethnic minorities, older adults without stable income, and migrant workers.
By official data, China declared the elimination of extreme poverty nationally in 2020. However, relative poverty and regional disparities persist, especially in western provinces and mountainous areas where infrastructure and access to services are limited.
Causes of Neediness in China
1. Geographical and Regional Disparities
Eastern China, especially along the coast, enjoys robust economic growth, while western and central regions lag behind. These less developed regions suffer from fewer job opportunities and poorer living conditions.
2. Rural-Urban Gap
The rapid urbanization has attracted many to cities, but many rural areas face low agricultural productivity and limited access to education and healthcare, which perpetuates poverty cycles.
3. Aging Population
China’s rapidly aging society creates a vulnerable group of elderly people who often lack sufficient pension and social security support, especially in rural areas.
4. Migration and Social Exclusion
Migrant workers moving to cities to find jobs frequently encounter unstable living conditions, lack of social welfare, and inadequate healthcare, contributing to economic vulnerability.
Challenges Faced by the Needy in China
- Limited access to quality education and healthcare in impoverished areas
- Insufficient social security coverage for rural residents and elderly
- Economic vulnerability from unstable employment, especially among migrants
- Environmental degradation affecting agricultural productivity in poor regions
Government Efforts and Poverty Reduction Policies
China has implemented a broad range of policies to combat poverty and support the needy:
- Targeted Poverty Alleviation Programs that focus on improving infrastructure, education, healthcare, and employment in poor areas.
- Relocation Projects moving residents from ecologically fragile or isolated regions to better locations with more opportunities.
- Social Welfare Improvements including expanded pension schemes and healthcare coverage.
- Rural Revitalization Strategy aimed at sustainable development in agriculture and rural communities.
These efforts have shown success in dramatically reducing extreme poverty and improving living standards.
Conclusion
Despite its impressive economic growth, China still faces significant challenges in fully eradicating neediness. Structural issues like regional inequality, rural-urban divide, and social security gaps require ongoing attention. The Chinese government’s focused policies have achieved substantial reductions in poverty, yet achieving balanced development and social security for all remains a critical goal. Continued investment in education, healthcare, infrastructure, and social protections will be essential to support China’s vulnerable populations in the years ahead.
Helping the needy in Venezuela with ،Tether
TRC20 - USDT
TDYwNu4SbmPaLuJEw3oLQNFFyAmqA3Yvog